Assoc. Prof. Ekrem GUNER

Dear colleagues,
I am honored to share with you the first issue of 2026 (volume 6, issue 1) of the Grand Journal of Urology (Grand J Urol)
with the contributions of many respected researchers and authors.
Grand Journal of Urology (GJU) aims to carry written and visualscientific urology studies to academic platforms and to
make significant contributions to the science of urology. Our journal has been abstracted/indexed in Tubitak Ulakbim TR
Index, EBSCOhost, J-Gate, SciLit, ResearchGate and Google Scholar international databases. As of these achievements,
the Grand Journal of Urology (GJU) has taken its place among the journals indexed by national and international databases.
In this issue of our journal, there are many valuable articles under the subheadings of Andrology, Endourology, General
Urology, Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgery, Pediatric Urology, Reconstructive Urology and Urologic Oncology. I hope
that these carefully prepared articles will make important contributions to valuable readers, researchers and the urology
literature.
On this occasion, I would like to express my heartfelt gratitude to our authors who have contributed to our journal with
their articles, to our reviewers who have meticulously evaluate the articles.
Respectfully yours
January 2026
Assoc. Prof. Ekrem GUNER, MD
Editor-in-Chief
Onursal Varlıklı, Mustafa Alper Akay, Necla Gürbüz Sarıkaş, et al.
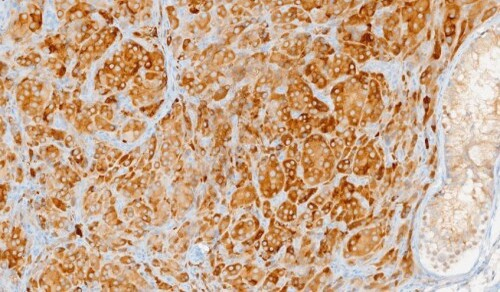
Testicular microlithiasis (TM) is a pathological
condition characterized by diffuse calcification within the
seminiferous tubules [,]. Research on TM in pediatric
populations is limited, and its association with testicular
disease in children remains a subject of debate. [,,]. TM
is observed in 1.1-4.2% of asymptomatic males without
urological disorders [,,]. In the testicular parenchyma,
it is usually detected by US and is typified by hyperechoic
non-shadowing foci that are 1-3 mm in diameter. Although
the exact cause of calcified material inside seminiferous
tubules is unknown, several theories have been proposed,
including inflammation, poor Sertoli cell phagocytosis,
excessive immunological response, and rapid cell renewal
[]. Epidemiological studies have indicated an increased
prevalence of TM in patients with risk factors for testicular
tumor development. Its association with various benign or
malignant pathologies has been documented, particularly
testicular germ cell tumors, cryptorchidism, testicular torsion
or atrophy, gonadal dysgenesis, varicocele, Klinefelter"s
syndrome, Down"s syndrome, infertility, male pseudohermaphroditism,
carcinoma in situ, and a family or personal
history of testicular cancer [,].
In asymptomatic patients, TM is typically identified
incidentally during routine medical examinations or US
performed for other diagnostic purposes. Symptomatic TM
is defined as the presence of microliths on US, accompanied
by testicular pain, testicular edema, increased testicular size,
hydrocele, varicocele, or testicular atrophy, which can occur
at any age [,].
We performed a retrospective analysis of the clinical
characteristics, comorbidities, follow-up, and outcomes of
patients with TM as observed on scrotal US. The objective
of this study was to examine the relationship between TM
and histopathological findings.
Mehmet Özay Özgür, İbrahim Halil Baloğlu, Gökçe Karlı, et al.
Childhood (
Çağatay Özsoy, Mücahit Gelmiş, Erhan Ateş

In recent years, rapid advances in artificial intelligence
(AI) technologies, particularly large language models (LLMs),
have transformed the landscape of information processing and
decision making across various fields, including healthcare
[]. Since its release, the first globally recognized LLM-based
chatbot, ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI in November 2022,
has garnered millions of users []. Subsequently, several other
chatbots have been introduced, including Copilot (formerly
Bing Chat, developed by Microsoft in February 2023), Claude
(developed by Anthropic in March 2023), and Gemini (formerly
Bard, developed by Google in December 2023). These chatbots
have demonstrated a remarkable capability to understand and
generate human-like texts across diverse domains. Recent
studies have shown that chatbots perform exceptionally well in
comprehending medical concepts [].
In the field of urology, chatbot applications remain relatively
nascent but are rapidly gaining attention. Emerging research
suggests that chatbots can assist in patient counseling for various
urological conditions, including benign prostatic hyperplasia,
urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, and prostate
cancer [-]. For instance, chatbots can be trained to provide
interactive explanations about treatment options, potential side
effects, or preprocedural preparations for interventions, such
as onabotulinum toxin injections, sacral neuromodulation,
or robotic radical prostatectomy [,]. They may also aid in
interpreting laboratory or imaging results, guiding patients on
medication adherence or follow-up schedules, and supporting
lifestyle interventions for recurrent stone disease or lower
urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) [,]. Additionally, from a
professional education perspective, chatbots are being explored
as tools for medical students and urology residents, including
guideline-based content and clinical case simulations [].
Recent investigations have also assessed whether chatbot
responses align with clinical practice guidelines, such as those
issued by the European Association of Urology [].
Bibliometrics, a snapshot of scholarly literature within
a defined period, offers a quantitative method for analyzing
scientific output and research trends. This strategy allows
scholars to uncover prominent authors, high-impact journals,
notable institutions, and emerging research themes by analyzing
indicators, such as publication volume, citation trends, and coauthorship
patterns [].
Despite growing interest in this subject, no comprehensive
assessment has yet been conducted on chatbot-related scientific
output in the field of urology. Our study represents the first
bibliometric analysis specifically focused on this emerging area.
Understanding the development of this interdisciplinary field,
situated at the intersection of urology, artificial intelligence, and
digital health, is essential to guide future research directions and
facilitate clinical integration.
Ali Atan, Murat Yavuz Koparal, Ender Cem Bulut, et al.
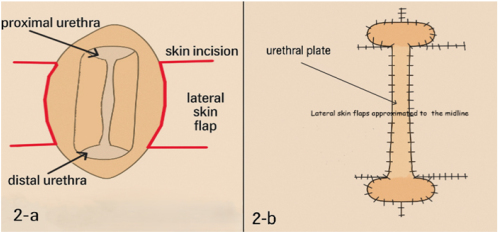
Urethral stricture disease (USD) is a common and complex
condition characterized by narrowing of the urethral lumen due
to scar tissue formation following urethral injury. The etiology
of USD includes external trauma, genitourinary infections,
inflammatory dermatological conditions, pelvic radiotherapy,
and iatrogenic factors such as urethral instrumentation and
endoscopic surgery [,]. Although USD can occur in any
segment of the male urethra, the bulbar (43%) and penile (37%)
segments are most frequently affected [].
The management of bulbar urethral strictures remains
a subject of debate, primarily due to the heterogeneous
characteristics of the strictures and variations in surgeon
preference. There is no universally accepted optimal procedure
for all patients with bulbar urethral stricture. The appropriate
repair strategy should be selected based on stricture length,
urethral lumen width, the degree of spongiofibrosis, and the
underlying etiology [,]. Excision and primary anastomosis
(EPA) tension-free is considered the most effective surgical
option for short bulbar urethral strictures measuring < 2 cm [].
For strictures > 2 cm in length, substitution urethroplasty using
grafts or flaps are required.
Substitution urethroplasty can be performed using either
single-stage or staged procedures []. Single-stage repair is
generally appropriate for simple strictures, whereas staged
procedures may be necessary for more complex disease [].
Fuchs et al. reported a preference for single-stage repair
in most cases, with only 30% of patients requiring staged
reconstruction []. Although the frequency of staged procedures
has decreased substantially, they remain an important option in
urethral reconstructive surgery. Several critical factors must be
considered when deciding between a single-stage and staged
approach, including the condition of the urethral plate, the extent
of spongiofibrosis, the length of the harvested graft, chordee
formation, and the suitability of the urethral graft bed [].
The precise definition of severe bulbar urethral stricture
remains a topic of discussion, as highlighted in the most recent
EAU guidelines []. Palminteri et al. suggested that a urethral
plate measuring less than 3 mm should be classified as a severe
stricture, and that severe urethral strictures encompass highgrade,
nearly obliterative, and obliterative types []. Hoy et
al. also emphasized that two-stage repair is necessary in cases
of lichen sclerosus, a history of multiple failed hypospadias
repairs, or the presence of an obliterated or nearly obliterated
urethral lumen []. In this study, we report our experience with
staged repair using scrotal or penile skin flap urethroplasty in
patients with severe bulbar urethral stricture.
Tugay Aksakallı, Adem Utlu, Şaban Oğuz Demirdöğen, et al.
Urolithiasis represents one of the leading causes of
morbidity in urological practice, and its incidence has been
steadily increasing worldwide [,]. Currently, miniaturized
ureterorenoscopes represent the preferred approach for ureteral
calculi, given their high efficacy and favorable safety profile
[]. In contrast, for proximal ureteral stones
Mehmet Sefa Altay, Adem Utlu, Ahmet Emre Cinislioğlu, et al.
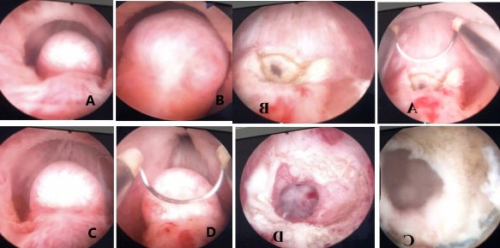
Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive despite one
year of regular, unprotected intercourse and affects 4–17% of
couples worldwide [,]. Male factors contribute to nearly half
of infertility cases, with approximately 20% of infertile men
exhibiting severe oligospermia or azoospermia [,].
The causes of male infertility are classified as pre-testicular,
testicular, and post-testicular []. Midline prostatic cysts are
considered a correctable post-testicular cause of male infertility
[]. These cysts can lead to partial or complete ejaculatory
duct obstruction (EDO) []. EDO is identified in 1–5% of
men with obstructive infertility []. Patients typically present
with azoospermia and/or aspermia []. Diagnosis is primarily
made using transrectal ultrasonography (TRUS) or magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI) [].
Aspermia is defined as the absence of semen during
ejaculation, whereas hypovolemic ejaculate refers to an ejaculate
volume of less than 0.5 mL. Both conditions are among the rarest
causes of male infertility [,]. EDOs are included among the
obstructive causes of aspermia, and the primary surgical treatment
for this condition is transurethral ejaculatory duct resection (TURED).
Although alternative approaches such as TRUS-guided cyst
aspiration or laser incision have been attempted, their outcomes
have not proven as effective as TUR-ED [].
TUR-ED is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure
that reopens the obstructed ejaculatory duct, facilitating sperm
passage []. However, limited studies have evaluated the longterm
efficacy of this procedure and its impact on fertility, with
most available research being case reports. In this study, we
aimed to assess the long-term outcomes of TUR-ED in patients
with aspermia or hypovolemic ejaculate due to midline prostatic
cysts who presented to our clinic with infertility.
Murat Şambel, Çağatay Özsoy, Selim Taş, et al.
Varicocele, defined as the dilation and reflux of the
pampiniform plexus veins, represents the most common and
surgically correctable cause of male infertility []. It is identified
in approximately 15% of men with primary infertility and up
to 80% of those with secondary infertility []. The detrimental
effects of varicocele on spermatogenesis have long been
recognized, with several pathophysiological mechanisms, such
as testicular hyperthermia, increased oxidative stress, hormonal
dysfunction, and venous stasis, proposed to underlie impaired
testicular function [].
Although physical examination remains the cornerstone
of diagnosis, its observer-dependent nature limits diagnostic
accuracy []. Therefore, scrotal color Doppler ultrasonography
(CDUS) has become a widely accepted complementary tool for
confirming varicocele and assessing its severity []. Scrotal color
Doppler ultrasonography provides an objective and quantitative
assessment that supports clinical examination, as emphasized in
previous reports []. In routine practice, a venous diameter >3
mm and reflux lasting longer than 2 seconds during the Valsalva
maneuver are commonly regarded as diagnostic thresholds for
clinical varicocele [,]. Furthermore, Schiff et al. reported in
2006 that patients with a venous diameter ≥3 mm accompanied
by Valsalva-induced reflux experienced significant postoperative
improvements in sperm count and motility [].
However, the extent to which ultrasonographically measured
venous diameters correspond to the actual macroscopic and
morphological characteristics of dilated veins removed during
surgery remains insufficiently investigated [,]. Only one
study to date has shown that intraoperative venous diameters
are systematically underestimated by preoperative CDUS [].
The relationship between surgically measured venous size and
postoperative semen improvement, or broader clinical infertility
outcomes, thus remains unclear, representing a notable gap in
the literature.
Our study aims to address this gap by evaluating the
correlation between preoperative CDUS findings and
intraoperative venous measurements, as well as exploring the
association between surgically measured venous dimensions
and postoperative semen parameters.
Parth Shah, Siddharth Yadav, Harshdeep Singh, et al.
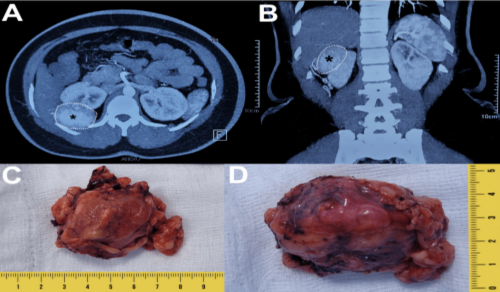
Approximately 20% of renal masses clinically suspected
to be malignant are ultimately identified as benign on final
histopathological examination following surgical resection [].
Angioleiomyomas are benign smooth muscle tumors that most
commonly arise in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, while their
occurrence in visceral organs, including the kidney, is exceedingly
rare []. Despite their rarity, angioleiomyomas represent the most
common benign mesenchymal tumors of the kidney. To date,
fewer than five cases of renal angioleiomyoma have been reported
in the literature. This highlights the rarity and diagnostic challenge
posed by this entity. Herein, we report an unusual case of renal
angioleiomyoma in a young female. We emphasize the importance
of distinguishing it from its malignant mimics, particularly renal
cell carcinoma with angioleiomyoma-like stroma (RCC-AMLSt),
as well as other morphologically similar renal tumors. Accurate
diagnosis is crucial to prevent unnecessary aggressive treatment
and ensure effective patient management.
Pieter De Rop, Sander Tilli
The horseshoe kidney (HSK) is a well-known yet
insufficiently understood renal anomaly. Although higher
incidences arise in men, families with renal anomalies or Turner
Syndrome (14-20%), no clear genetic predisposition has been
found. General incidence is around 0.15-0.45% [,].
During the embryogenesis horseshoe kidneys evolve from
a fusion of the kidneys, most often at the lower pole (90%),
connected by an isthmus consisting of functional parenchyma
or fibrous tissue [,]. HSK could receive vascularisation from
the aorta, common iliac artery, inferior and superior mesenteric
artery or sacral artery. Often multiple branches are encountered
for both poles and separate isthmic branches [-]. Venous
malformations arise most often from the inferior vena cava
(IVC), where double IVC, left IVC and pre-isthmic IVC are
possible [,]. Ureteral duplications, alternated positions in
combination with different calyceal positions are often seen
and could cause infections, UPJ obstruction or nephrolithiasis
[]. The diagnostic pathway for these pathologies occasionally
uncovers an incidental tumour diagnosis. Tumours of the
HSK are primarily renal cel carcinoma (RCC) and urothelial
carcinoma, but more rare tumours like Wilms tumour and
carcinoid tumour have higher incidences in HSK compared to
the general population. The risk of developing urothelial cell
carcinoma in HSK is four times higher, due to recurrent urinary
tract infections and chronic inflammation because of stone
formation and hydronephrosis [].
Multiple treatment options exist in the management of renal
cell carcinoma. The gold standard for small (< 7cm) lesions in
normal shaped kidneys with chronic kidney disease remains
the partial nephrectomy []. Robot-assisted laparoscopy is
the preferred technique for performing partial nephrectomy,
offering comparable oncological outcomes to open or standard
laparoscopic approaches, but with a significantly lower
complication rate []. Treatment of RCC in HSK remains to
have a case-based approach, to date no guideline exists.
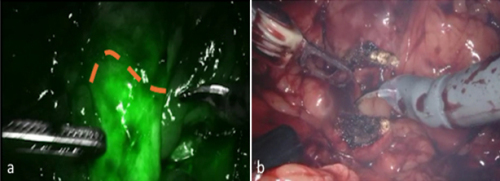
In this report we present the case of a robot-assisted
partial nephrectomy of a solid renal mass combined with an
isthmectomy while using indocyanine green (ICG) fluorescence
to demarcate the isthmus.